Assembly Theory and Life Analysis
Examining Molecular Assembly Theory and Definitions for Life
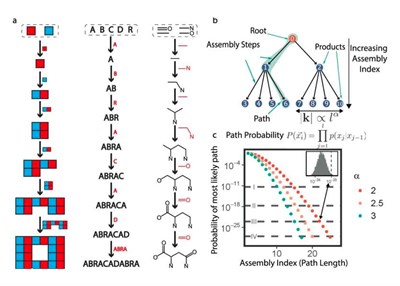 Assembly Theory characterizes a 3D material objects degree of life or conscious design, based on a mathematical measurement of complexity of its construction. It is primarily focused on molecular design, though the concept can be extended down to the subatomic, quantum level.
Assembly Theory characterizes a 3D material objects degree of life or conscious design, based on a mathematical measurement of complexity of its construction. It is primarily focused on molecular design, though the concept can be extended down to the subatomic, quantum level.
The general idea is that we can measure, through mass spectrometry or otherwise, how complex an object or life form is. We can determine, based on the complexity of its assembly, and the amount of copies of it in the environment, whether it exhibits signs of life, or conscious design -- we can measure "bio-signatures" by comparing the order in a system, compared with the probabilistic natural possibilities of randomness.
If we witness a cluster of 3D constructs (similar creatures/beings), or measure coordinated 4D time motions (ie: motion of bird flocks), we can infer, through assembly theory, the "level of life" or "level of consciousness" in that system. Complex patterns stand out from the random background of possibilities.
Advanced chemical / electrical / molecular processes like photosynthesis, carbon and nitrogen fixation, replication, chiral enrichment, and morphogenesis can be detected by their molecular complexity, and are "bio-signatures" which we can look for to identify life.
 Taken to its logical conclusions, Assembly Theory describes a universe which can "assemble itself" into life, through some form of conscious will. This aligns with the Consciocentric Paradigm, and is compatible with the idea that conscious design directs the collective motions of the many-verse, driving evolution, order and life.
Taken to its logical conclusions, Assembly Theory describes a universe which can "assemble itself" into life, through some form of conscious will. This aligns with the Consciocentric Paradigm, and is compatible with the idea that conscious design directs the collective motions of the many-verse, driving evolution, order and life.
From unique molecular constructs and protein strands, through RNA/DNA chromosomes, to cellular organisms, to multi organ creatures and advanced life, each stage on the path shows increasing molecular patterns which clearly diverge from the background noise of randomness or entropy in the universe.
Assembly Theory Publishing in Nature Magazine:
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-021-23258-x
Identifying molecules as bio-signatures with assembly theory (Nature):
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-021-23258-x.pdf